When the heart is in this. Diastole represents ventricular filling and systole represents ventricular contractionejection.
Cardiac Cycle Physiology Diagram Phases Of The Cardiac Cycle
The human heart beats over 100000 times per day.

. Cardiac myocytes do not contract during diastole and this is when the majority of blood fills the heart chambers. Systole is defined as the phase in which the heart especially the ventricles is contracting. Ventricular relaxation called.
There are 2 main phases to the heart cycle - diastole and systole. Each part of the cardiac cycle consists of several phases characterized by either. In order to achieve this high output efficiently the heart works through a carefully controlled sequence with every heart beat this.
This is also known. Outflow phase the ventricles continue to contract pushing blood into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole.
The different phases of the cardiac cycle involve. List the three types of the muscles. The first article in this section regards the cardiac cycle in overview.
Systole and diastole occur in both the right and left heart though with very different pressures see. At rest the heart pumps around 5L of blood around the body every minute but this can increase massively during exercise. There are two phases of a heartbeat.
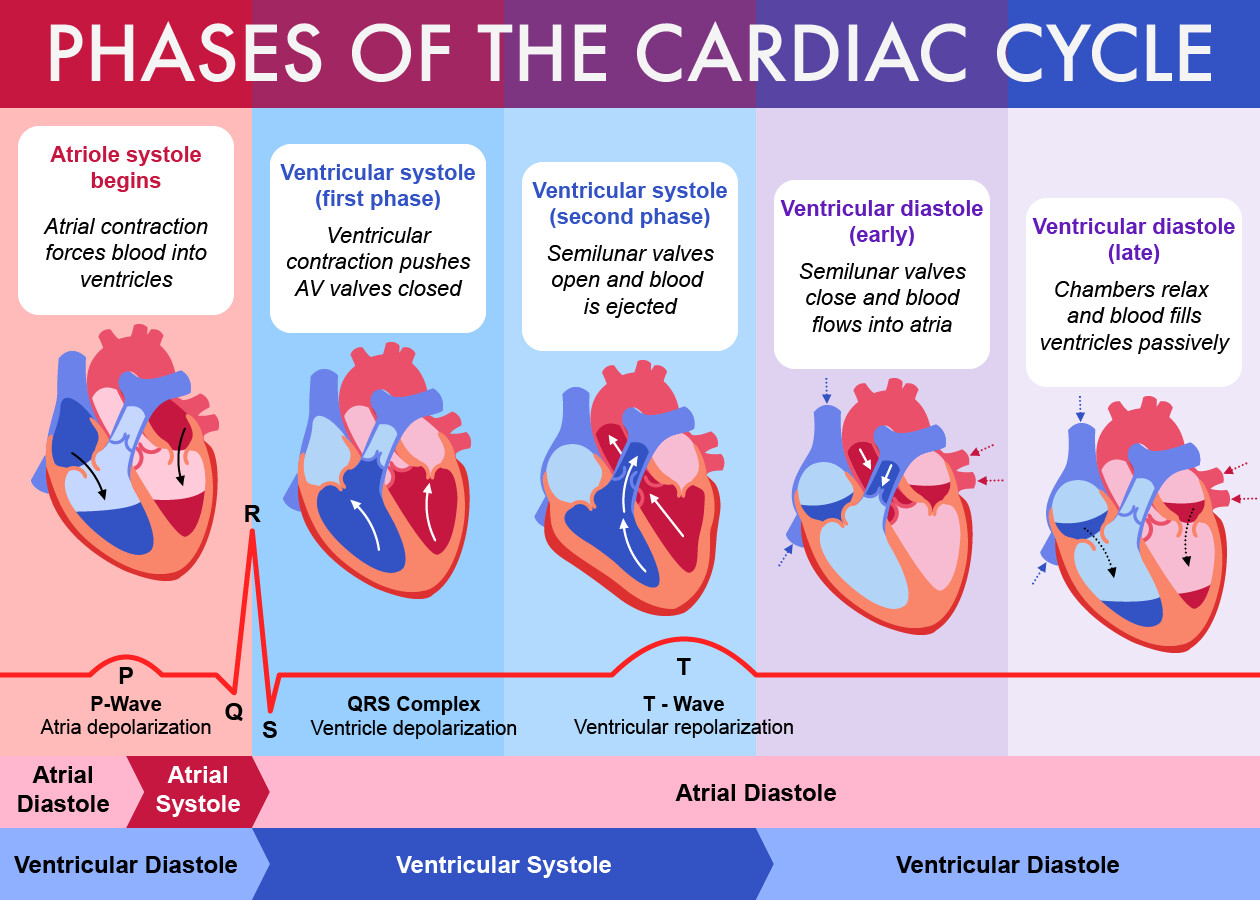
Atrial and Ventricular diastole chambers are relaxed and filling with blood Atrial systole atria contract and remaining blood is pushed into ventricles Ventricular systole ventricles contract and push blood out through aorta and pulmonary artery. Early ventricular systole ventricle contracts atria relaxes semilunar valves still closed. Filling phase the ventricles fill during diastole and atrial systole.
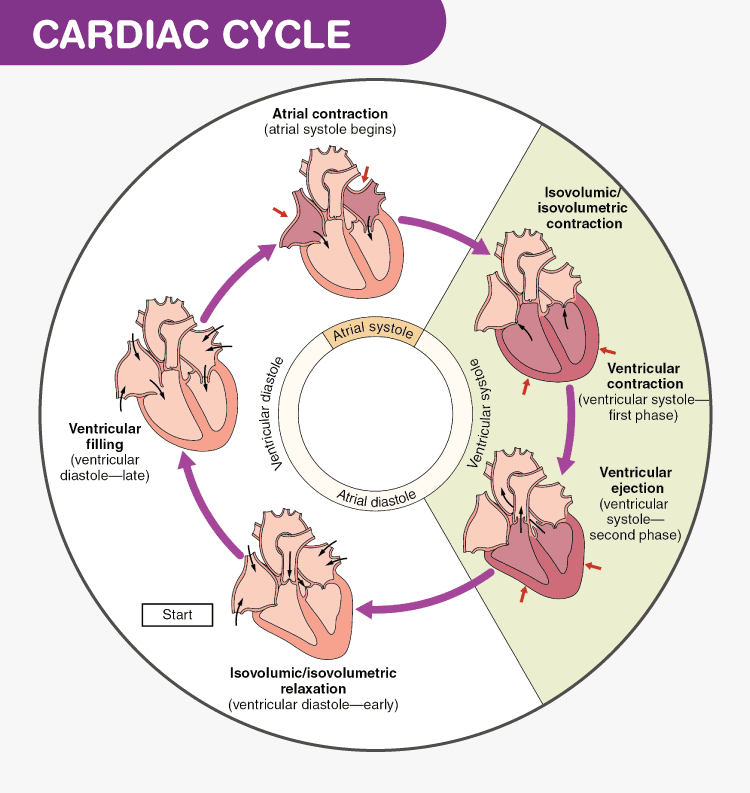
The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Isovolumetric contraction the ventricles contract building up pressure ready to pump blood into the aortapulmonary trunk. The period of time that begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle.
The cardiac cycle can be divided into four stages. The cardiac cycle is a period from the beginning of one heart beat to the beginning of the next one. Atrial systole is when blood is pumped into the ventricles whereas ventricles pump blood into the aorta that transports blood to the rest of the body during ventricular systole.
Atrial systole atria contracts which forces blood into the ventricles. There are three stages to the cardiac cycle. Phase III is known as the period of ejection and begins at point D.
This complete cycle comprises 5 main stages. Both the atria and ventricles undergo systole and diastole and it. Rapid ventricular filling phase.
During systole the myocytes contract and eject blood from the particular chamber either into other heart chambers or into the vascular system. In each cardiac cycle the heart contracts systole pushing out the blood and pumping it through the body. The cardiac cycle consists of two phases.
The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. Terms in this set 11 What are the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle. Phase I is called the period of filling and begins at point A when diastolic filling begins.
Both the atria and. Diastole is the term used to describe the relaxation of the heart. Describe the cardiac cycle atrial systole.
Group of answer choices Isovolumetric contraction Ventricular ejection Ventricular filling. The standard pressurevolume loop for a single cardiac cycle is divided into four phases. Increased atrial pressure tricuspid and mitral valves are open ventricular filling occurs ventricular systole.
Atrial systole ventricular systole and ventricular diastole. Phases of cardiac cycle. The cardiac cycle is the coordination of the filling and emptying of the heart of blood by electrical signals that cause the heart muscles to contract and relax.
It consists of two parts. Ventricular contraction called. This is followed by a relaxation phase diastole where the heart.
Diastole is defined as the phase in which the heart especially the ventricles is at rest. Cardiac cycle events can be divided into diastole and systole. 4 rows Each cardiac cycle has a diastolic phase also called diastole where the heart chamber is in a.
The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. Phase II is known as the period of isovolumic contraction and begins at point C. The period of time that begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle Figure 631.
The period of timethat begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle Figure 1931. The relaxed heart allows for blood to fill the cardiac chambers. The AV valve opens while the semilunar valves closes.
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the ventricles begin to contract while the semilunar valves remain closed. Atrial diastole Atrial systole Isovolumic contraction Ventricular ejection Isovolumic relaxation Ventricular filling. The cardiac cycle has 3 stages.
The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Isovolumetric ventricular contraction all valves closed increased ventricular pressure pulmonary and aortic valves open ventricular emptying and atrial filling occur. A cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in a single heartbeat.
The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Late ventricular systole contraction of ventricles atria relaxes blood forces into the pulmonary artery and aorta.

19 3 Cardiac Cycle Anatomy Physiology

Cardiac Cycle Definition Phases And Quiz Biology Dictionary

0 Comments